Rare Element Resources
Bear Lodge Project
Canadian NI 43-101 Technical Report
October 9
th
, 2014
10135-200-46 - Rev. 0
14-41
14.14 Block Model Density Estimation
Densities were estimated for each block based on the fraction of FMR/carbonatite
mineralization, which was estimated using IDP estimation and the same procedure
used for estimating the rare-earth-element grades. The formulae used for the block
model density estimates are summarized in Table 14.24.
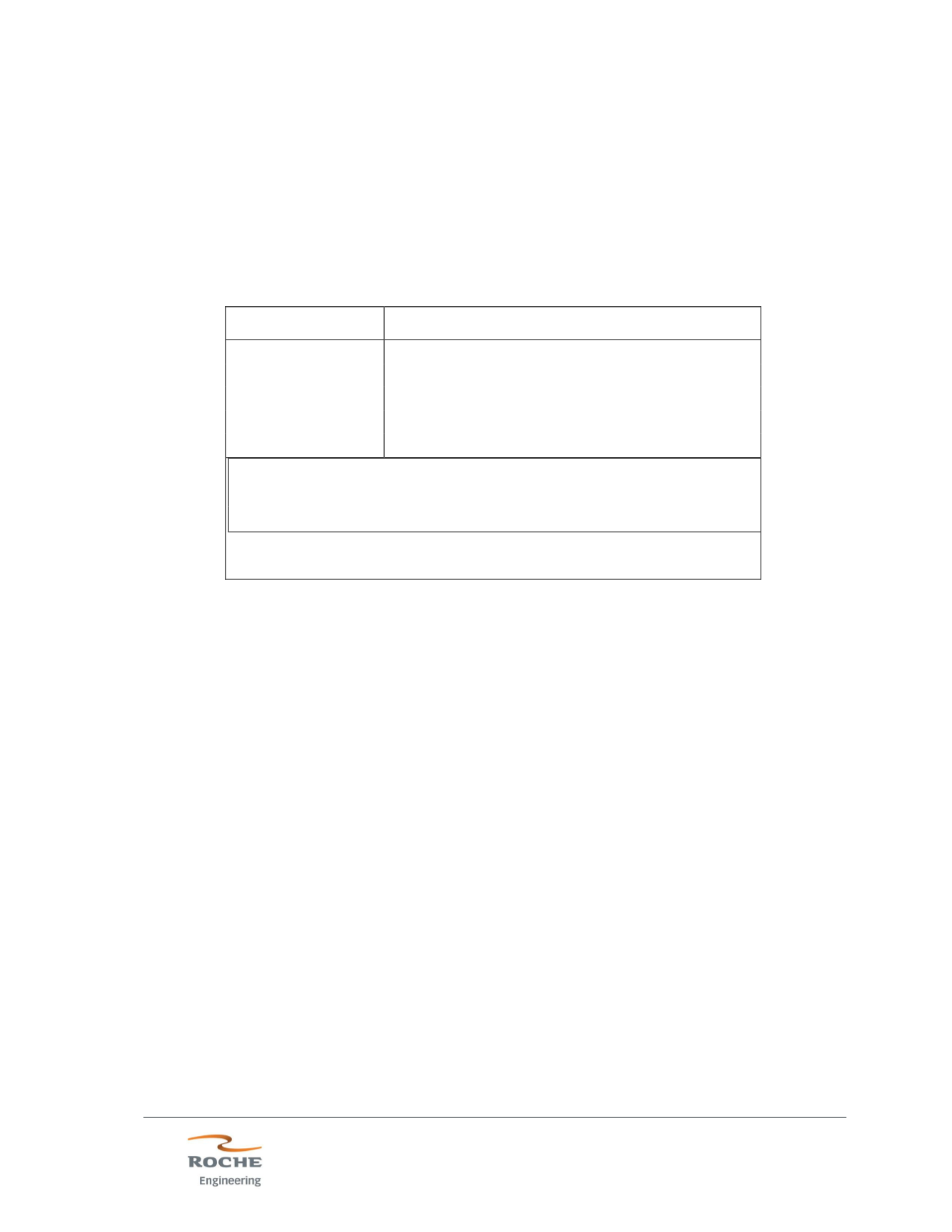
Table 14.24 - Formulae for Block Density Estimation
Oxidation Type
Density Formula (t/m
3
)
Overburden & Clay
1.8
Oxide
0.01*(REminIDP*1.81 + (100-REminIDP)*2.26)
OxCa
0.01*(REminIDP*2.16 + (100-REminIDP)*2.32)
Trans
0.01*(REminIDP*2.32 + (100-REminIDP)*2.55)
Sulfide
0.01*(REminIDP*2.91 + (100-REminIDP)*2.59)
Where, REminIDP is the IDP estimate of the percentage of FMR and
Carbonatite. Default density is assigned to blocks with no REminIDP
estimate using a value of zero (0.00) for REminIDP.
Metric densities are divided by 32.026735 to convert from t/m
3
to short
tons/ft
3
.
(A.Noble, 2014)
14.15 Dilution
Dilution is incorporated into the resource model through two separate mechanisms:
first, geometric dilution is incorporated by compositing; and second, volume-variance,
or block-smoothing dilution is incorporated by adjusting the parameters of the
inverse-distance-power grade estimation method.
The purpose of geometric dilution is to smooth out local geometric variability, to
enhance overall continuity by defining larger, more regular shapes, and to group the
data into higher-grade, primarily dike mineralization, and lower-grade, primarily
stockwork mineralization. In addition, mineable-width mineralized zones are created
for mine planning.
Geometric dilution is incorporated when true-width composites are computed using
20 to 30-foot minimum horizontal widths for definition of OreZONE codes. Compared
to the original assays, which are nominally five-feet long and broken at major
contacts, such as high-grade dikes, the OreZONE composites introduce 71% dilution
and reduce ore grade by 33%. In addition, there is a 21% loss of ore-grade intervals


