Occupational Dose Evaluation in Support of the Development of
October, 2012
Rare Element Resources, Inc. Bear Lodge Project
5
1.3.2
Sources of Naturally Occurring Radiation
Radiation is produced from naturally occurring radionuclides contained in all environmental
media. Natural uranium and thorium and their associated radioactive decay products are major
constituents of NORM and are most important when considering the ore at the BLP. Natural
uranium; i.e., uranium with natural isotopic abundances, consists primarily of uranium-238 and
uranium-234 (based on radioactivity) and to a lesser degree uranium-235. Table 1.1 shows the
natural isotopic abundance of each important uranium isotope based on mass and radioactivity.
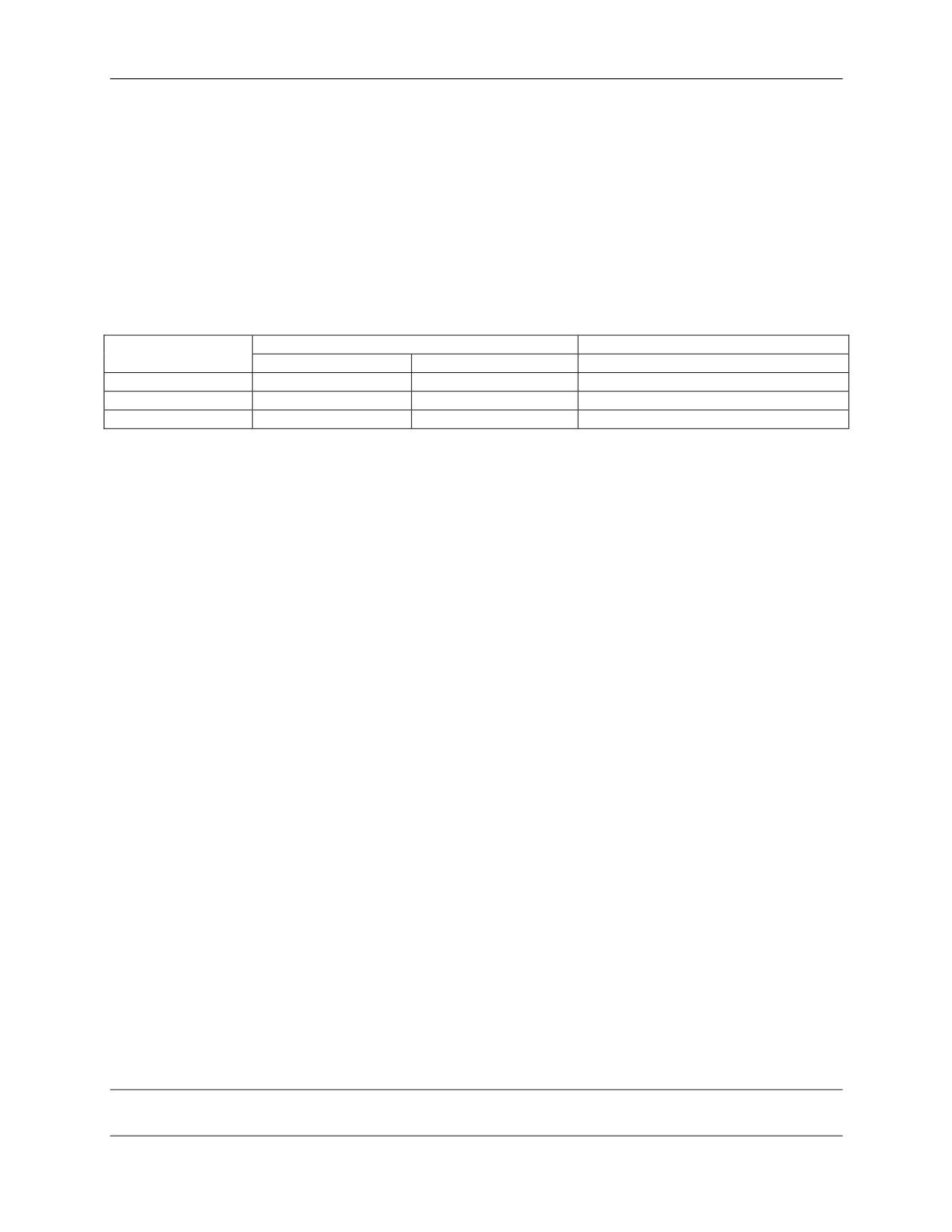
Table 1.1 Natural Abundances of Uranium Isotopes
Uranium Isotope
Abundance (%)
a
Mass
Radioactivity
Half-Life (y)
a
Uranium-238
99.28
48.6
4.5 x 10
9
Uranium-235
0.71
2.2
7.0 x 10
8
Uranium-234
0.0058
49.2
2.5 x10
5
a
Adopted from Eisenbud and Gesell, 1997
Starting with uranium-238, a series of 14 different radionuclides (including uranium-234) are
produced through radioactive decay until non-radioactive lead-206 is reached. This radioactive
decay chain is called the uranium-238 decay series and its radionuclides emit alpha, beta and
gamma radiation (Figure 1.3).
In terms of radiation dose to workers, one important member of the uranium-238 decay series is
radon-222. As a noble gas, radon-222 is chemically inert and --if formed in near-surface soil or
rock from the decay of radium-226-- is free to diffuse into the atmosphere. Radon-222 (and its
short-lived decay products) can accumulate inside homes or other structures and in the United
States (U.S.) is the largest contributor to background radiation dose from natural sources.
Generally, radon-222 is not a concern in the outdoor environment because of atmospheric
dispersion. Buildings with industrial processes often have high ventilation rates compared to
residential houses thereby mitigating the potential impacts of radon-222 within these facilities.
Natural thorium consists almost entirely of thorium-232 by mass. Like uranium-238, thorium-
232 is the first radionuclide in a decay series ending in non-radioactive lead-208. As shown in
Figure 1.4, there are 11 radionuclides in the series with decays resulting in emission of alpha,
beta and gamma radiation. Radon-220, known historically as thoron because it is in the thorium-
232 decay series, is an isotope of radon that is released to the atmosphere from radium-224 in
near-surface soil and rock. Due to its half-life of 55 seconds, radon-220 decays rapidly and --
coupled with atmospheric diffusion-- is generally not considered an occupational or
environmental concern.


